Describe the Chemistry of Starch Hydrolysis
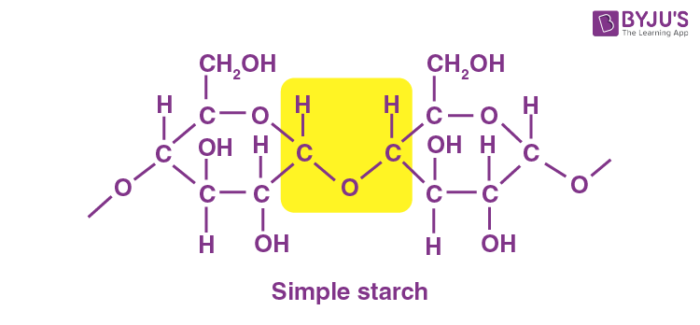
Amylose is an unbranched homopolysaccharide formed by about 5-600 glucose units linked by α-14 glycosidic bonds. Starch hydrolysis test is used to.
Starch Definition Formula Uses Facts With Examples
Describe something other than enzyme that will catalyze the hydrolysis of starch.
. Describe the function of hydrolases. It is present into vegetable cells and contains two types of homopolysaccharides amylose and amylopectin. A deep understanding of the effect of acid hydrolysis on starch structure and functionality is of great importance for starch scientific research and its industrial applications.
Describe the chemistry of starch hydrolysis. In the presence of the enzyme amylase and subsequent starch hydrolysis around the growth area there will be a yellow clearish zone AROUND the growthIn the absence of amylase the starch will not have been degraded so the. Take large molecules and break them into smaller molecules with the use of water or aqueous solution.
This book describes the different starch sources used commercially to produce glucose syrups leading onto the manufacture of these products principally by enzymic means. Amylase is an enzyme that attacks starch. It has a helix structure with six glucose units for turn is soluble in water and places in the core of the starch granules.
Starch solution 10 iodine solution 2M hydrochloric acid 1M sodium hydroxide Fehlings solution A Fehlings solution B 2 test tubes test tube rack hot water bath pipettes 24-well plate small beaker with rinsing water small waste water beaker. Converted to its monomers dextrose the dry mass. Describe the function of hydrolases.
Multiple glucose units are joined by glucosidic bonds. The smallest product of this. Starch consists of two ingredients-amylose and amylopectin.
Hydrolysis of starch This is a relatively simple practical that can be used to illustrate some of the chemistry covered in the Option B. Partial hydrolysis of amylopectin and amylose both. The chemical used to detect microbial starch hydrolysis on starch plates is 4.
It is suitable for both Standard and Higher Level students and gives some good chemistry to explain involving the structure and hydrolysis of starch and the redox reactions. Acid hydrolysis is a hydrolysis mechanism in organic chemistry in which protic acid is used to catalyse the cleavage of a chemical bond by means of a nucleophilic replacement reaction with the addition of water elements H2O. In the first part of the experiment acid and heat will be used to hydrolyze the starch chains.
Starch mixture Benedicts Test Iodine Test StarchSaliva S1 S2 StarchBuffer B1 B2 A-1. The end products depends on the strength of enzymes used and the common enzymes are α-Amylase which produces the disaccharide maltose and the trisaccharide maltotriose. Starch ---alpha-amylase--- glucose maltose dextrin.
Because of the large size of amylose and amylopectin molecules these organisms can not pass through the bacterial cell. 4 rows Starch Hydrolysis Test. Dextrins are shorter broken starch segments that form as the result of the random hydrolysis of internal glucosidic bonds.
Up to 24 cash back In this lab two different methods will be applied to break down starch molecules into smaller units containing of 2 to 3 glucose molecules. What does starch hydrolysis by a bacterium indicate. Describe what caused the observed results in the Benedicts Test for starchsaliva vs.
Starch consists of 2 componentsamylose and amylopectin which are present in various amounts. Whenever starch polysaccharides molecules undergo hydrolysis it forms either monosaccharides disaccharides or trisaccharides. Describe the chemistry of starch hydrolysis.
Amylose is a long linear chain of -D--glucose units joined by glycosidic association C1-C4 along-link. Depending on the relative location of the bond under attack as counted from the end of the chain the products of this digestive process are dextrin maltotriose maltose and glucose etc. To see if starch breaks up into glucose molecules.
Placing the agar plate on a white piece of paper or background will REALLY help you to distinguish the zones. Further chapters describe the physico-chemical and. Hydrolysis is the breaking of bigger molecules into smaller ones by reacting with water.
Of the solute increases by some 11 to 180 g. Starch Hydrolysis Test Principle Procedure Uses and Interpretation. Chemical structure of starch.
Acid hydrolysis is an important chemical modification that can significantly change the structural and functional properties of starch without disrupting its granular morphology. Starch is a complex polysaccharide found abundantly in plants and usually deposited in the form of large granules in the cytoplasm of the cell. In the conversion of.
Up to 256 cash back Get the detailed answer. Often used to differentiate species from the genera Clostridium and Bacillus. Amylopectin is a branched-chain polymer consisting of D-glucose units in which the chain is formed by glycosidic connection C1-C4 and glycosidic connection C1-C6 branches.
Up to 24 cash back Hydrolysis of Starch. Name _____ Section _____ 45 Part A. Indicate whether each test was positive or negative and indicate what color each solution was after performing the tests.
Starch is a polysaccharide of glucose. ASSESSMENT Critical Thinking and Learning Outcomes Review 1. Worldwide it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets and is contained in large amounts in staple foods such as wheat potatoes maize corn rice and cassava manioc.
Biochemistry sub-topic B4 Carbohydrates. Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bondsThis polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. This test is used to identify bacteria that can hydrolyze starch amylose and amylopectin using the enzymes a-amylase and oligo-16-glucosidase.
In the second part and enzyme will be used to break apart the starch chains.
What Products Are Made By Starch Hydrolysis Quora
No comments for "Describe the Chemistry of Starch Hydrolysis"
Post a Comment